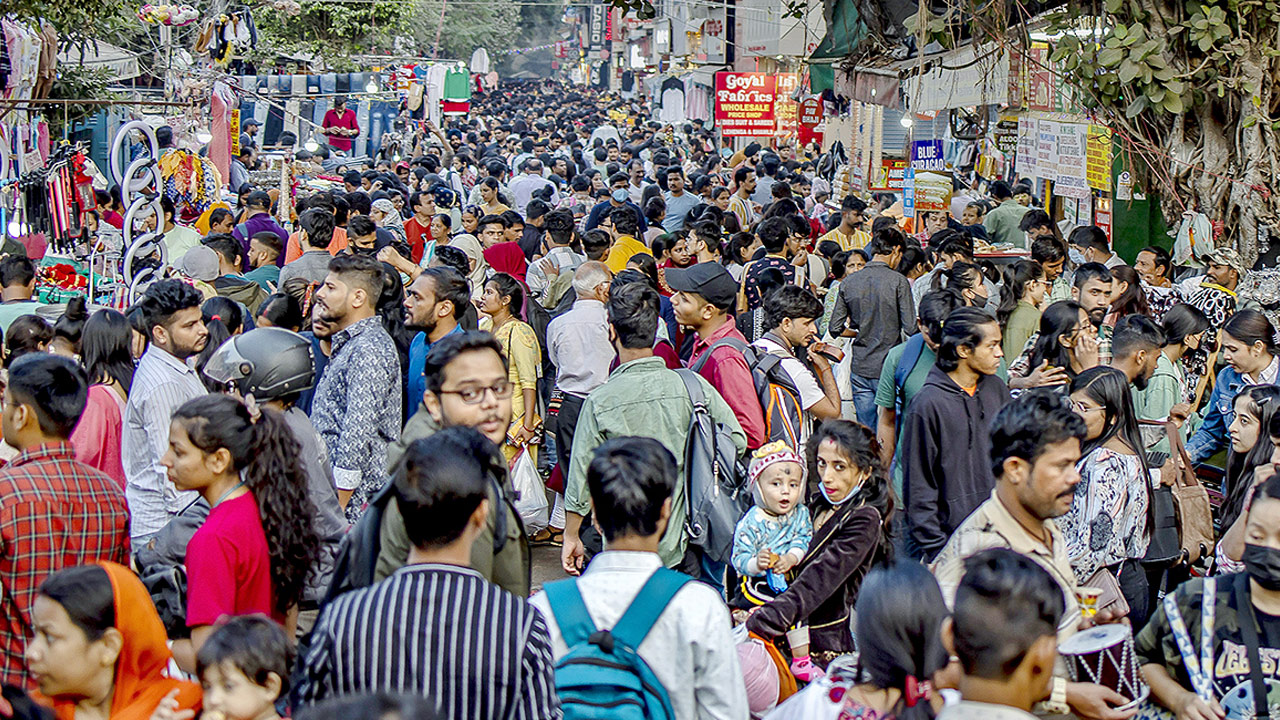
Unemployment is rising in many parts of the world, pushing people into poverty due to a lack of proper income opportunities. While some countries struggle with a growing population that challenges development, Europe faces a declining population, raising concerns about future labor shortages. Surveys predict that by 2100, Europe's population will significantly decrease due to factors like birth rates, aging, migration, and economic shifts. To counter this, European countries are introducing special policies to attract new populations and ensure economic stability. Experts analyze the reasons behind these demographic trends in Europe.
By 2100, Europe is expected to have one of the highest aging populations globally. Advances in healthcare are increasing life expectancy, leading to a rise in the proportion of elderly people. Countries like Germany, Italy, and Spain are already experiencing this trend. As older populations contribute less to productivity, social welfare systems, healthcare infrastructure, and pension schemes face immense pressure. Experts suggest comprehensive policy reforms to support aging societies and address these challenges effectively.
Birth rates are declining in many European countries, and this trend is expected to intensify in the coming decades. Social changes, economic stress, and lifestyle factors contribute to this decline. Countries like Greece, Portugal, and Hungary may struggle to maintain a stable workforce, leading to labor shortages and economic crises. To counteract this, governments must implement policies that promote higher birth rates and support working parents. Migration is also expected to play a crucial role in sustaining Europe's population by 2100, with countries like France, the UK, and Sweden working to attract immigrants to balance demographic challenges.